The Sustainable Future of Printing: Green Technologies and Practices
Printing has come a long way since the days of Gutenberg, but with progress comes environmental challenges. The printing industry, like many others, is now facing the imperative to become more sustainable. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of sustainable printing, exploring green technologies and practices that can help minimize the industry’s environmental impact.
Sustainability has become a central concern across industries, and the printing sector is no exception. Traditional printing methods have historically been associated with resource-intensive processes, such as paper production and chemical inks. As environmental awareness grows, the demand for sustainable printing solutions has increased significantly.
Sustainable printing, often referred to as “green printing,” encompasses a range of practices and technologies aimed at reducing the environmental footprint of printing operations. These efforts are driven by the need to conserve resources, reduce waste, and minimize the carbon emissions associated with printing.
Green Printing Technologies
One of the cornerstones of sustainable printing is the adoption of green technologies. These technologies are designed to minimize environmental impact while maintaining or even improving the quality of printed materials. Let’s explore some of these green printing technologies in greater detail:
1. Soy-Based Inks
Traditional inks contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that release harmful fumes into the atmosphere. Soy-based inks are a sustainable alternative, derived from renewable soybeans. They produce fewer VOCs, reduce air pollution, and are easier to recycle. Moreover, they offer vibrant colors and good print quality.
2. Waterless Printing
Waterless printing eliminates the need for dampening systems in offset printing, reducing water consumption and the generation of wastewater. This technology not only conserves water but also improves print quality and efficiency. It achieves this by relying on silicone-coated printing plates that repel ink from non-image areas.
3. UV Curing
UV curing involves the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to instantly dry inks and coatings on printed materials. This process is more energy-efficient than traditional drying methods, such as heat drying, and reduces harmful emissions. UV-cured inks also adhere better to various substrates, improving print quality and durability.
4. Digital Printing
Digital printing technologies, such as inkjet and laser printing, have gained popularity due to their ability to print on demand. This reduces paper waste associated with overproduction and allows for variable data printing, which further minimizes resource use. Digital printing’s ability to produce small print runs economically aligns with sustainable practices.
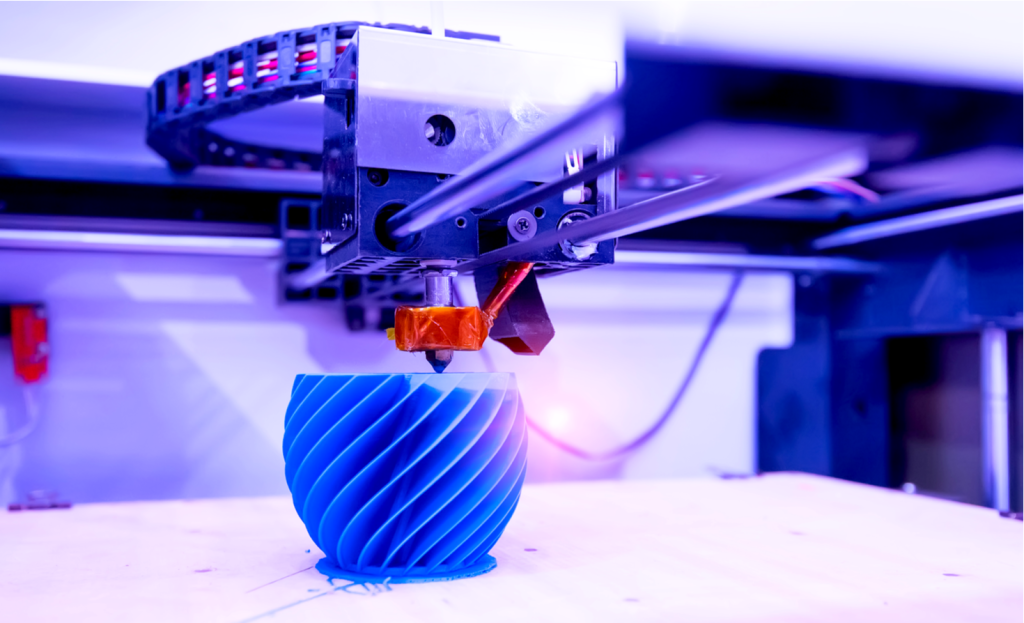
5. 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology with significant sustainability potential. It builds objects layer by layer, minimizing material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. Additionally, 3D printing enables the creation of complex, lightweight structures, further reducing material consumption.
Recycled and Alternative Materials
In addition to green printing technologies, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in sustainable printing practices. Printing companies are increasingly using recycled paper and alternative materials, such as bamboo or hemp paper, to reduce their environmental impact. Let’s delve deeper into these material choices:
6. Recycled Paper
Recycled paper reduces the demand for virgin pulp, which is often harvested from forests, helping to combat deforestation. It can be sourced from post-consumer waste, pre-consumer waste (such as trimmings from the printing process), or a combination of both. High-quality recycled paper is now readily available for various printing applications.
7. Alternative Sustainable Substrates
The use of sustainable substrates, such as biodegradable or compostable materials, is also gaining traction. These materials break down naturally, reducing landfill waste and the long-term environmental impact of printed products. For instance, packaging made from biodegradable materials is becoming increasingly popular, particularly for eco-conscious brands.
Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a significant concern in the printing industry. High-speed presses and large-scale printing facilities can be energy-intensive. However, sustainable printing practices aim to address this issue by promoting energy-efficient equipment and processes:
8. LED UV Curing
LED UV curing systems consume less energy compared to traditional drying methods. They also produce less heat, reducing the load on air conditioning systems in printing facilities. LED technology offers instant on/off capabilities, reducing energy consumption during standby periods.
9. On-Demand Printing
On-demand printing minimizes energy consumption by producing only the required quantity of printed materials. This contrasts with traditional printing, which often involves large print runs, leading to excess inventory and waste. On-demand printing reduces the need for storage space and associated energy usage.
10. Energy-Efficient Equipment
Printing companies are investing in energy-efficient printing equipment, including printers with sleep modes and automatic shutdown features, further reducing energy consumption during periods of inactivity. Energy-efficient HVAC systems and lighting are also part of sustainability efforts in printing facilities.
Waste Reduction

Reducing waste is a fundamental aspect of sustainable printing. Traditional printing processes often result in significant waste, including misprints, overruns, and obsolete materials. Green printing practices aim to minimize waste generation:
11. Digital Printing for Short Runs
Digital printing is well-suited for short print runs, as it eliminates the need for costly setup processes and plates used in offset printing. This reduces the amount of paper and ink wasted on overproduction. Digital printing also allows for just-in-time production, further reducing the need for large inventories.
12. Print-On-Demand Services
Print-on-demand services allow materials to be printed as needed, reducing the need for large print runs and the associated waste of excess inventory. This approach aligns with the principles of sustainability and cost-effectiveness. It also reduces the need for warehousing space and transportation-related emissions.
13. Waste Recycling Programs
Many printing companies have implemented comprehensive waste recycling programs, including the recycling of paper waste, empty ink cartridges, and obsolete equipment. These programs divert materials from landfills and reduce the industry’s environmental impact. Some companies have even developed closed-loop recycling systems, where waste materials are reintroduced into the production process.
Certifications and Standards
Certifications and industry standards play a vital role in ensuring that sustainable printing practices are followed. Two prominent certifications in the sustainable printing industry are:
14. Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Certification
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification ensures that paper and wood products come from responsibly managed forests. Printers that use FSC-certified paper are supporting sustainable forestry practices. The FSC label on printed materials reassures consumers that the paper comes from environmentally responsible sources.
15. ISO 14001 Environmental Management
ISO 14001 is an internationally recognized standard for environmental management systems. Printers that adhere to ISO 14001 have implemented processes to minimize their environmental impact, from waste reduction to energy efficiency. ISO 14001 certification demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and responsible environmental stewardship.
Case Studies
To illustrate the practical implementation of sustainable printing practices, let’s examine a few case studies of companies that have successfully adopted green printing methods:
Case Study 1: Eco-Friendly Packaging
A packaging company adopted waterless printing and soy-based inks for their product packaging. This not only reduced their environmental
impact but also attracted environmentally-conscious consumers, boosting sales. The shift to eco-friendly packaging aligned with their brand’s commitment to sustainability.
Case Study 2: Digital Book Printing
A book publisher shifted to digital book printing for smaller print runs, eliminating the need for large-scale offset printing. This reduced waste, lowered costs, and allowed for more frequent updates of educational materials. The publisher found that digital printing also provided greater flexibility in responding to market demands.
Case Study 3: Green Marketing Materials
A marketing agency embraced sustainable printing practices for its promotional materials. By using recycled paper and environmentally-friendly inks, they were able to position themselves as an eco-conscious agency, attracting clients with similar values. The agency’s commitment to sustainability became a selling point in a competitive industry.
Case Study 4: Sustainable Direct Mail
A direct mail marketing company reduced its carbon footprint by using targeted mailing lists and digital printing. This approach allowed for personalized, environmentally-friendly direct mail campaigns. By reducing the number of unsolicited mailings, the company improved its relationship with recipients and decreased printing and postage costs.
Consumer Awareness
The growing awareness of environmental issues and consumer demand for eco-friendly products are driving the adoption of sustainable printing practices. Consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on the sustainability credentials of printed materials. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, printing companies are responding by offering eco-friendly options and prominently displaying their sustainability certifications. The alignment of consumer values with sustainable printing practices is a powerful force for positive change in the industry.
Challenges and Barriers
While sustainable printing offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and barriers that printing companies may encounter when transitioning to green practices:
16. Initial Costs
Investing in green technologies and materials can be costly upfront. Many printing companies may hesitate due to concerns about the initial financial outlay. However, it’s important to view these investments as long-term strategies that can lead to cost savings and improved competitiveness.
17. Resistance to Change
Adopting sustainable practices often requires a shift in mindset and workflow. Resistance to change from employees and management can be a barrier to implementing green printing methods. Effective communication and training programs can help overcome this resistance and foster a culture of sustainability within the organization.
18. Limited Availability
In some regions, access to sustainable materials and technologies may be limited. Printing companies may face challenges in sourcing eco-friendly materials and inks. Collaboration with suppliers and industry associations can help address these supply chain limitations.
19. Quality Concerns
There may be concerns about the quality and performance of sustainable materials and technologies compared to traditional options. Ensuring that green alternatives meet or exceed quality standards is essential. Conducting thorough testing and quality assurance procedures can help dispel these concerns.
Future Trends
The sustainable printing landscape continues to evolve, and several emerging trends are shaping its future:
20. Multi-Material Printing
Advancements in 3D printing technology are enabling multi-material printing, allowing for more complex and sustainable product designs. This capability is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace, where lightweight, durable materials are essential.
21. Bioprinting
Bioprinting is a cutting-edge field that uses 3D printing to create living tissues and organs. This technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare and reduce the need for organ transplants. Bioprinting demonstrates how 3D printing can be applied to highly specialized and sustainable applications.
22. Renewable Energy in Printing Facilities
Printing companies are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce their carbon footprint. These sources not only provide a sustainable energy supply but also demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility.
Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives play a critical role in promoting sustainable printing practices and raising awareness within the industry. Industry associations, educational institutions, and sustainability-focused organizations are actively involved in advancing knowledge and best practices in sustainable printing:
23. Industry Associations
Industry associations, such as the Printing Industries of America (PIA), are actively promoting sustainability in printing. They offer resources, training, and certifications to help printing companies adopt sustainable practices.
24. Educational Institutions
Educational institutions are integrating sustainability into their printing and graphic arts programs. They are training the next generation of printing professionals to understand and implement eco-friendly practices in their careers.
25. Research and Development
Research institutions and companies are investing in research and development to discover new sustainable printing materials and technologies. These efforts are essential for pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainable printing.
The journey towards sustainable printing is an ongoing process, driven by a growing awareness of environmental issues, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and technological advancements. Green printing technologies, materials, and practices are not only reducing the industry’s environmental impact but also improving cost-efficiency and competitiveness.
As printing companies and consumers alike embrace sustainability, the printing industry is poised to play a crucial role in the global transition to a more environmentally responsible future. By adopting and advocating for sustainable printing practices, we can preserve our planet’s resources while continuing to enjoy the benefits of printed materials in our daily lives.


Leave feedback about this